graphql 教程
GraphQL正在成为在现代web和移动应用程序中使用api的新方式;
GraphQL vs REST: 一个小案例
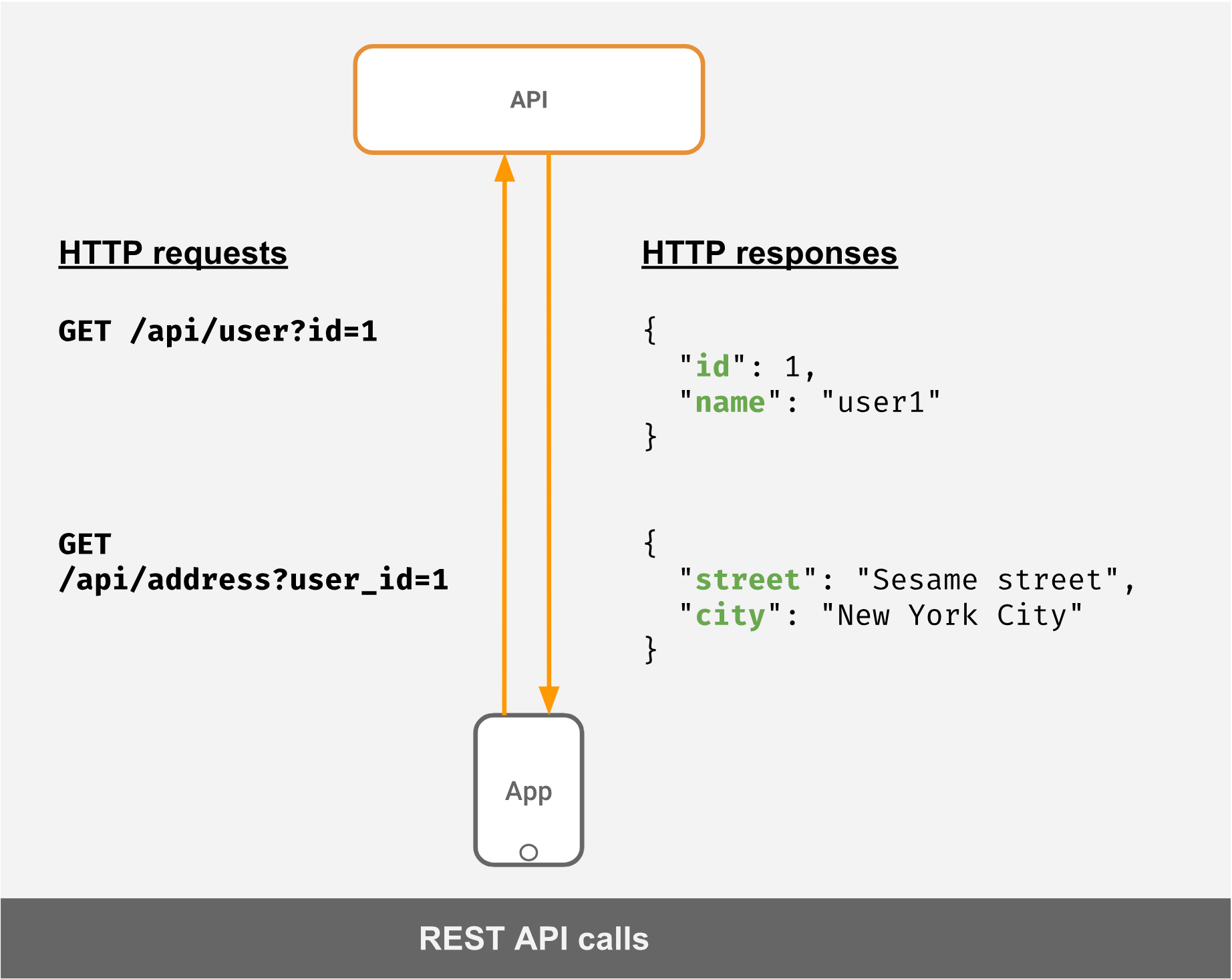
grahpql example
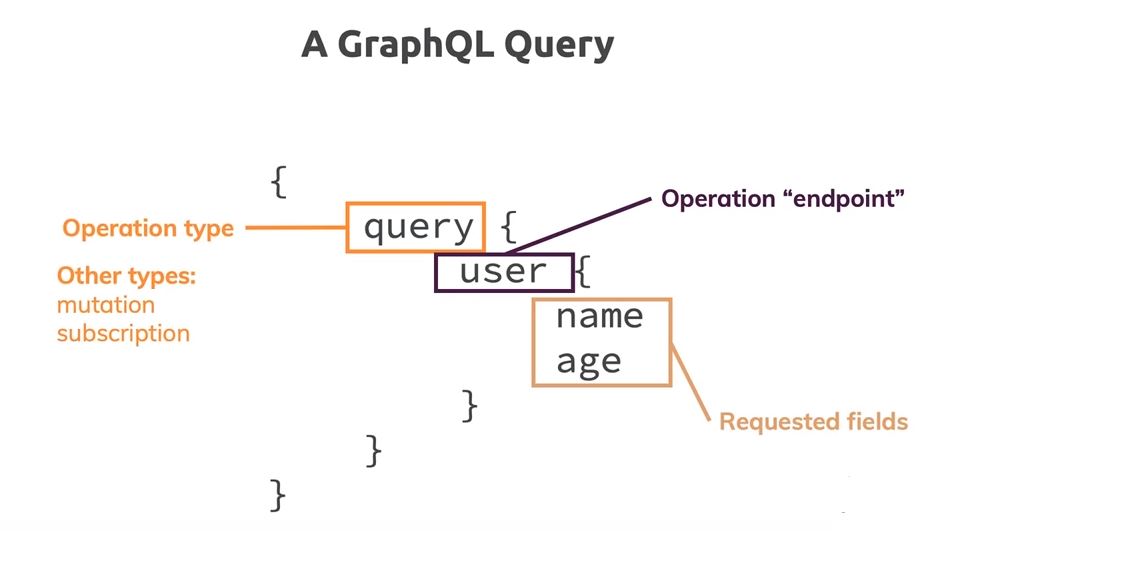
schema's types
GraphQL schema defines what types of data a client can read and write to your data graph
type Launch {id: ID!site: Stringmission: Missionrocket: RocketisBooked: Boolean!}
The Launch object type has a collection of fields, and each field has a type of its own. A field's type can be either an object type or a scalar type. A scalar type is a primitive (like ID, String, Boolean, or Int) that resolves to a single value. In addition to GraphQL's built-in scalar types, you can define custom scalar types.
An exclamation point (!) after a declared field's type means "this field's value can never be null."
type User {id: ID!email: String!trips: [Launch]!}
If a declared field's type is in [Square Brackets], it's an array of the specified type. If an array has an exclamation point after it, the array cannot be null, but it can be empty.
type Mission {name: StringmissionPatch(size: PatchSize): String}enum PatchSize {SMALLLARGE}
The missionPatch field of the Mission type takes an argument named size, which is of the enum type PatchSize. When you query for a field that takes an argument, the field's value can vary depending on the provided argument's value. In this case, the value you provide for size will determine which size of the mission's associated patch is returned (the SMALL size or the LARGE size).
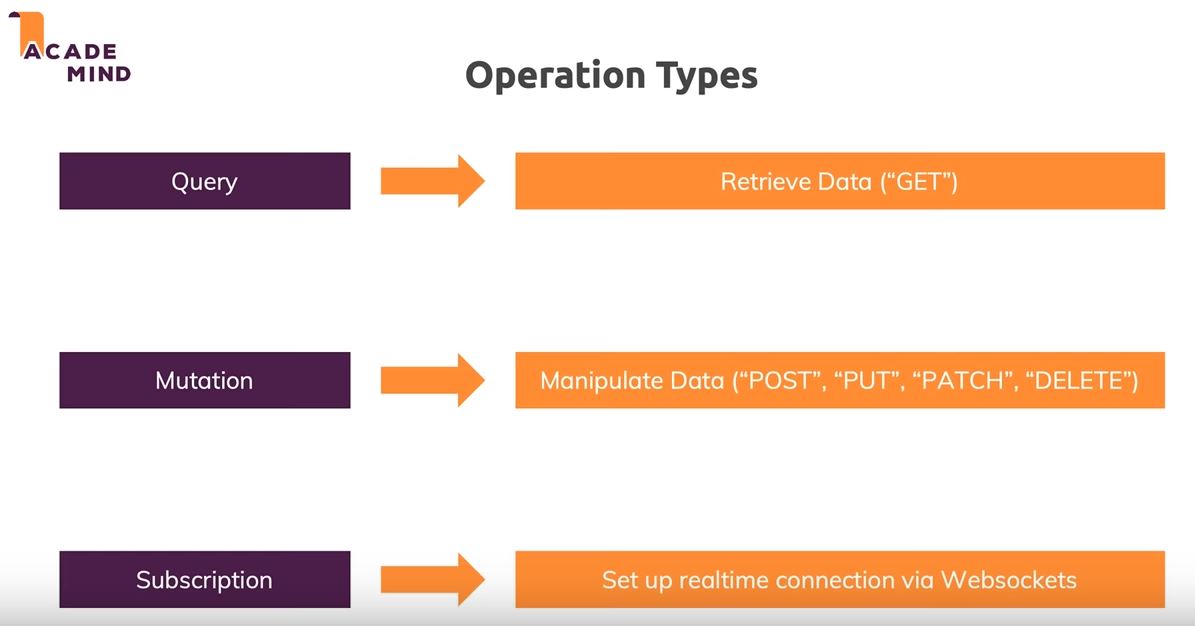
The Query type
our schema needs to define queries that clients can execute against the data graph
You define your data graph's supported queries as fields of a special type called the Query type
type Query {launches: [Launch]!launch(id: ID!): Launchme: User}
This Query type defines three available queries for clients to execute: launches, launch, and me.
The Mutation type
Queries enable clients to fetch data, but not to modify data. To enable clients to modify data, our schema needs to define some mutations.
The Mutation type is a special type that's similar in structure to the Query type.
type Mutation {bookTrips(launchIds: [ID]!): TripUpdateResponse!cancelTrip(launchId: ID!): TripUpdateResponse!login(email: String): String # login token}
Input types
In the GraphQL schema language, input types look exactly the same as regular object types, but with the keyword input instead of type: 当做mutation操作时,比如创建user,创建用户所传的参数就可以当做一个 input type,
input CreateUserInput {name: String!username: String!age: Int!nationality: Nationality = BRAZIL}enum Nationality {CANADABRAZILINDIAGERMANYCHILE}// 注意 开头是 input 关键词而不是 type// input 中可以设置默认值,比如这里的nationality为Nationality 类型,如果不传默认为BRAZIL
server side
resolver
const resolvers = {Query: {user(parent, args, contextValue, info) {return users.find((user) => user.id === args.id);},},Mutation: {createUser: (parent, args, contextValue, info) => {const user = args.createUserInput;const lastId = UserList[UserList.length - 1].id;user.id = lastId + 1;console.log(user)return user},}};// 注意获取前端传过来的参数的方式,在第二个参数中(args),比如在Mutation的createUser 中const user = args.createUserInput;// 这是前端传的{"createUserInput": {"name": "new name","username": "new username","age": 8}}// 这里是 type 定义文件type Mutation {createUser(createUserInput: CreateUserInput!): User}