网络性能重要指标
Web Vitals are a set of useful metrics that aim to capture the user experience of a web page. The following web vitals are all included:
Time to First Byte (TTFB)
First Contentful Paint (FCP)
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
LCP measures how long it takes for the largest content element (e.g. a hero image or heading text) on your page to become visible within your visitors' viewport.
First Input Delay (FID)
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
CLS indicates how much layout shift is experienced by visitors as your page loads.
前端性能优化
DOMContentLoaded 与 load事件
DOMContentLoadedThe DOMContentLoaded event is fired when the initial HTML document has been completely loaded and parsed, without waiting for stylesheets, images, and subframes to finish loading.loadThe load event is fired when a resource and its dependent resources have finished loading.window.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', (event) => {console.log('DOMContentLoaded --- DOM fully loaded and parsed');});DOMContentLoaded 相当于 jQuery ready() MethodjQuery ready() 兼容性更好,考虑到了老的IE浏览器等场景$(document).ready(function(){//your code});window.addEventListener('load', (event) => {console.log('load ---- page is fully loaded with images etc');});
async defer in script
With async (asynchronous), browser will continue to load the HTML page and render it while the browser load the script at the same time, but block parsing html when execute the script.带 async 的script 下载时,不会block html 的渲染,但一旦下载完成后执行script 时,html 的渲染会暂停async scripts load in the background and run when ready. The DOM and other scripts don’t wait for them, and they don’t wait for anything. A fully independent script that runs when loaded.带async的脚本一定会在load事件之前执行,可能会在DOMContentLoaded之前或之后执行。带 defer 的脚本和普通脚本(不带 defer 属性)的脚本一样,一定会在 DOMContentLoaded之前执行.async 使用场景:第三方脚本如:广告脚本<!-- Google Analytics is usually added like this --><script async src="https://google-analytics.com/analytics.js"></script>With defer , browser will run your script when the page finished parsing. (not necessary finishing downloading all image filesScripts with defer never block the page.Scripts with defer always execute when the DOM is ready, but before DOMContentLoaded event.defer脚本会在文档渲染完毕后,DOMContentLoaded事件调用前执行。The defer attribute is only for external scriptsThe defer attribute is ignored if the <script> tag has no src.在加载多个JS脚本的时候,async是无顺序的加载,而defer是有顺序的加载。

http缓存
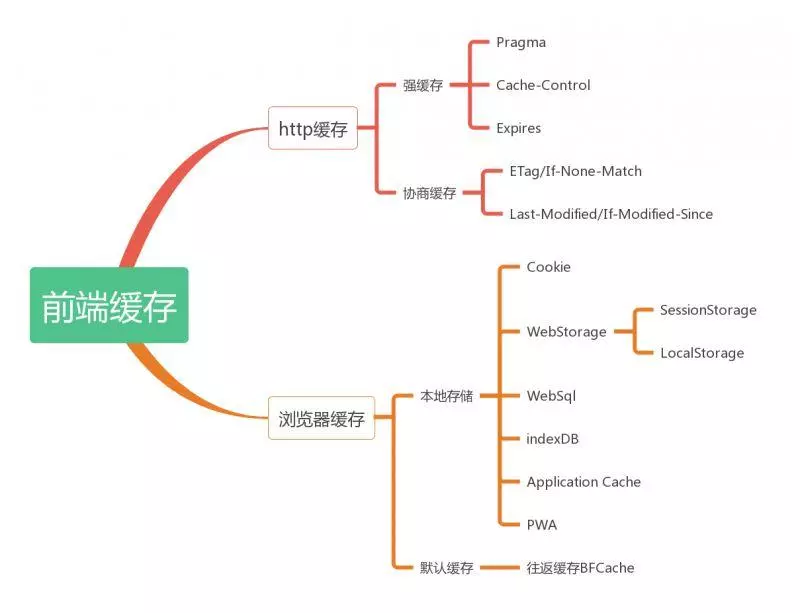
缓存分为强缓存协商缓存
强缓存
2个属性控制强缓存Expires和Cache-Control:max-age=<seconds>Expires是http 1.0定义的,使用的是相对时间,如果2边与服务器时间不统一就会出现问题,为了解决这个问题于是就出现了http 1.1定义的Cache-Control: max-age,这个属性使用的是相对时间,一般来说都是2个都加,然后取相对时间属性。Expires 的值对应一个 GMT (格林尼治时间),比如 “Mon, 22 Mar 2017 11:12:01 GMT” 来告诉浏览器资源缓存过期时间,如果还没有超过该时间点则不发请求,直接返回 200 OK。(from cache)Pragma和Cache-control共存时,Pragma的优先级是比Expires高的。Expires 两个致命的缺点:Expires 定义的缓存时间是相对于服务器上的时间而言的,而浏览器在判断的时候是基于客户端的系统时间的,如果用户修改了自己电脑的系统时间,那么这个缓存时间将没有任何意义。假如客户端上某个资源缓存时间过期了,但此时其实服务器并没有更新过该资源,那么这时候客户端要求服务器重新把东西再发送过来一遍,会浪费带宽和时间,这显然是不合理的,我们需要有一种正确的机制用来判断东西到底可以直接使用缓存。若报文中同时出现 Pragma、Expires 和 Cache-Control,那么会以 Cache-Control 为准
协商缓存
协商缓存是先向服务器询问下是否文件有更新,根据服务器的提示来决定是否使用缓存,由于比强缓存多了去服务器询问这一步所以势必没有强缓存快。协商缓存也有2对属性,分别是ETag和If-None-Match,Last-Modified和If-Modified-Since,每次请求的时候,浏览器会保存获取的ETag和Last-Modified,下次在调的时候会传If-None-Match和If-Modified-Since过去,值就是上次获取ETag和Last-Modified的值,然后根据返回的值是否有变化来决定是否取缓存的数据,Last-Modified是用时间来判断,ETag用标识符,之所以出现2个是因为Last-Modified只能精确到秒,如果1秒内有多次数据调用,它就无能为力了,所以出现了进阶的ETag,使用协商缓存的时候status显示的是304如果 Last-Modified 和 ETag 同时被使用,则要求它们的验证都必须通过才会返回304,若其中某个验证没通过,则服务器会按常规返回资源实体及200状态码。ETag 适合重要量小的资源Last-Modified 适合不重要的量大的资源 (比如一些图片等静态文件的修改,如果每次扫描内容生成 ETag 来比较,显然要比直接比较修改时间慢很多)
根据是否需要重新向服务器发起请求来分类,可分为(强制缓存,协商缓存), 强制缓存如果生效,不需要再和服务器发生交互,而协商缓存不管是否生效,都需要与服务端发生交互
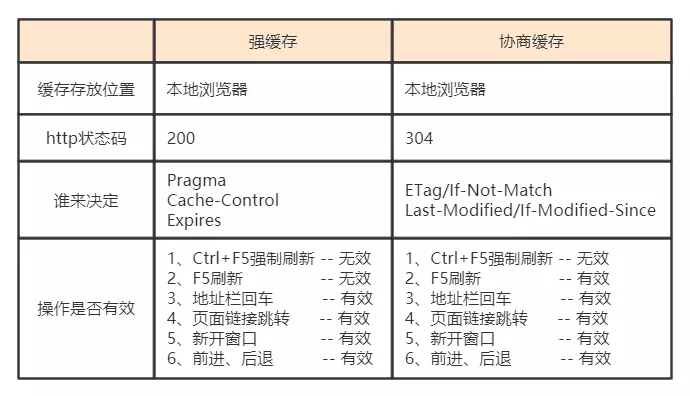
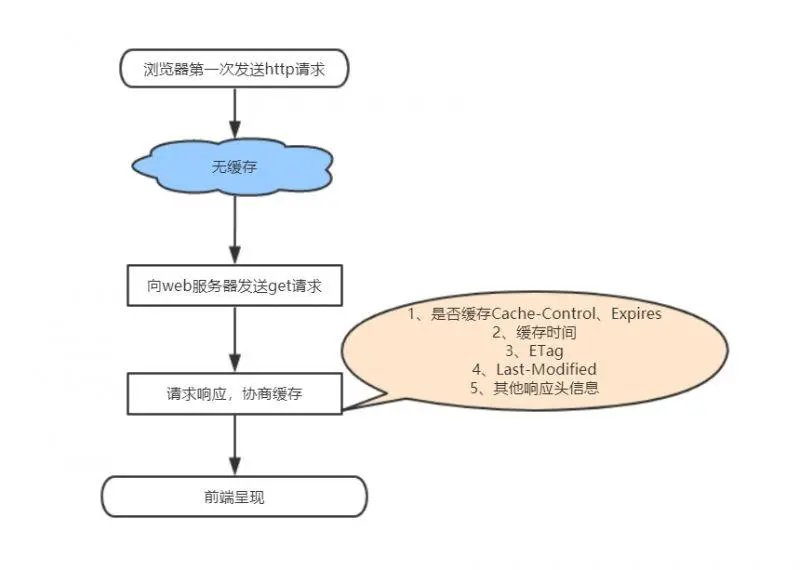
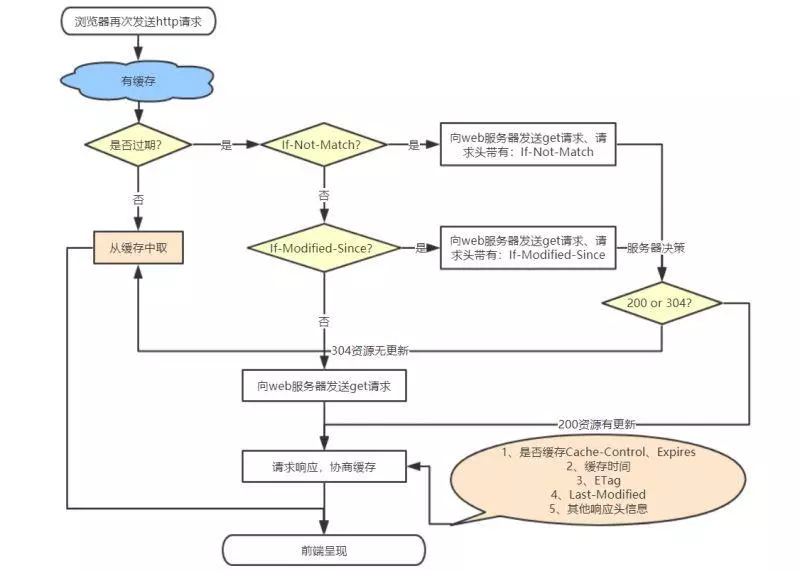
在chrome浏览器中返回的200状态会有两种情况:1、from memory cache(从内存中获取/一般缓存更新频率较高的js、图片、字体等资源)2、from disk cache(从磁盘中获取/一般缓存更新频率较低的js、css等资源)这两种情况是chrome自身的一种缓存策略,这也是为什么chrome浏览器响应的快的原因。其他浏览返回的是已缓存状态,没有标识是从哪获取的缓存。
前端压力测试
use preconnect and dns-prefetch
如果明确知道需要某个域名下的资源可以使用preconnect 和dns-prefetch 提前连接和解析dns
<!-- Preconnect to cdn.a.com --><link rel="preconnect" href="https://cdn.a.com" crossorigin /><!-- Fallback dns-prefetch for older browsers --><link rel="dns-prefetch" href="https://cdn.a.com" />
preload
<link rel="preload" href="https://cdn.a.com/hero-image.jpg" as="image" crossorigin /><link rel="preload" href="https://cdn.a.com/main.css" as="style" crossorigin />// 根据屏幕尺寸预加载不同内容<link rel="preload" as="image" href="https://cdn.a.com/a-lg.jpg" media="(min-width: 641px)" crossorigin><link rel="preload" as="image" href="https://cdn.a.com/a-sm.jpg" media="(max-width: 640px)" crossorigin>
What types of content can be preloaded?
Many content types can be preloaded. The possible as attribute values are:
fetch: Resource to be accessed by a fetch or XHR request, such as an ArrayBuffer, WebAssembly binary, or JSON file.font: Font file.image: Image file.script: JavaScript file.style: CSS stylesheet.track: WebVTT file.
preload video
对于link 标签, rel="preload" as="video" 在很多浏览器已经不再支持了, 可以使用video 的preload 属性
<video preload="auto|metadata|none">auto The author thinks that the browser should load the entire video when the page loadsmetadata The author thinks that the browser should load only metadata when the page loadsnone The author thinks that the browser should NOT load the video when the page loads
动态加载不同video 案例
<div id="responsive-video"></div><script>const video = document.createElement('video');video.autoplay = true;video.muted = true;video.loop = true;video.playsInline = true;video.preload = 'auto';video.style.width = '100%';// Choose video source based on screen widthif (window.innerWidth < 640) {// Mobilevideo.src = 'https://cdn.a.com/videos-sm.mp4';video.className = 'sm:hidden';} else {// Desktopvideo.src = 'https://cdn.a.com/videos-lg.mp4';video.className = 'hidden sm:block';}document.getElementById('responsive-video').appendChild(video);</script>